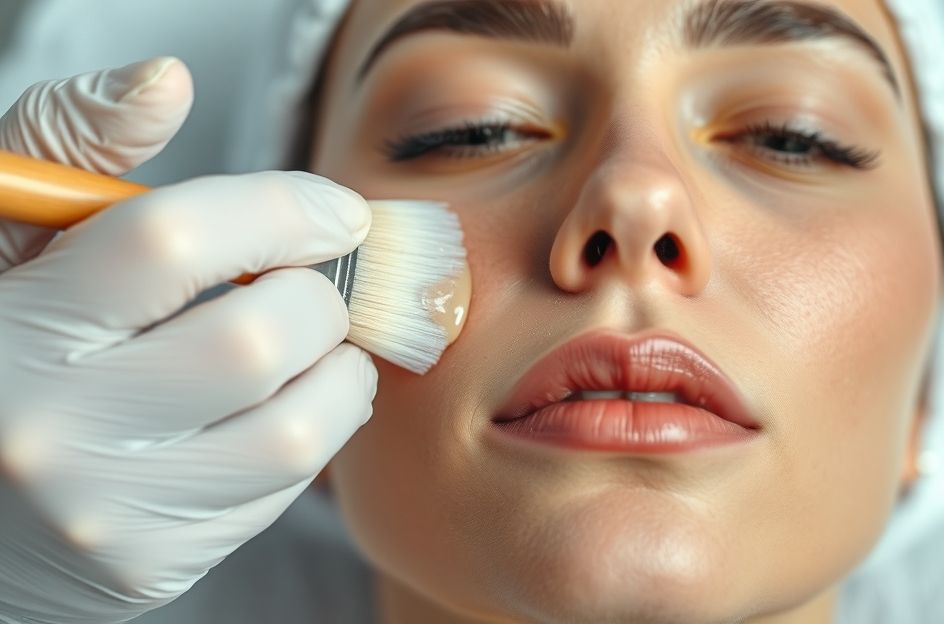
Chemical peels are a popular skincare treatment used by dermatologists to rejuvenate skin damaged by sun exposure, pigmentation issues, and wrinkles. The process involves applying a chemical solution to the skin, which causes the outer layers to peel away, revealing fresher, younger-looking skin beneath. However, it’s crucial to understand that while chemical peels can significantly improve the appearance of your skin, they do not halt or reverse the internal aging process. The primary benefit is the removal of old, damaged skin, paving the way for a revitalized complexion. Maintaining the results of a chemical peel requires diligent skincare, including protection from the sun’s harmful rays. Neglecting sun protection will lead to renewed skin damage, negating the benefits of the treatment.
Chemical peels are effective in addressing various skin concerns, such as mild wrinkles, sunspots, pigmentation irregularities, and a leathery skin texture. They can also diminish pre-cancerous spots and certain types of facial scars. In some instances, mild chemical peels are used as a treatment for acne.
While generally safe, chemical peels carry a risk of complications such as infection and scarring in rare cases. It’s essential to discuss these potential risks with your doctor before undergoing the procedure. Different chemical formulations are used to achieve varying depths of peeling. AHA (alpha-hydroxy acid) peels are superficial, TCA (trichloroacetic acid) peels offer a medium depth, and phenol peels penetrate the deepest. The choice of peel depends on the severity of the skin problem being addressed. Superficial peels are suitable for surface-level imperfections, while deeper peels are reserved for more pronounced scars. Your doctor will assess your skin condition, discuss your desired outcomes, and consider your tolerance for downtime and discomfort to determine the most appropriate type of peel. Deeper peels typically involve greater discomfort but yield more dramatic results.
*Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. It is not a substitute for professional medical consultation. Always consult with your doctor regarding any medical concerns. Any tips or recommendations provided in this article should only be followed after consulting with a healthcare professional. The author is not liable for any consequences or damages resulting from the use of information presented in this article.*